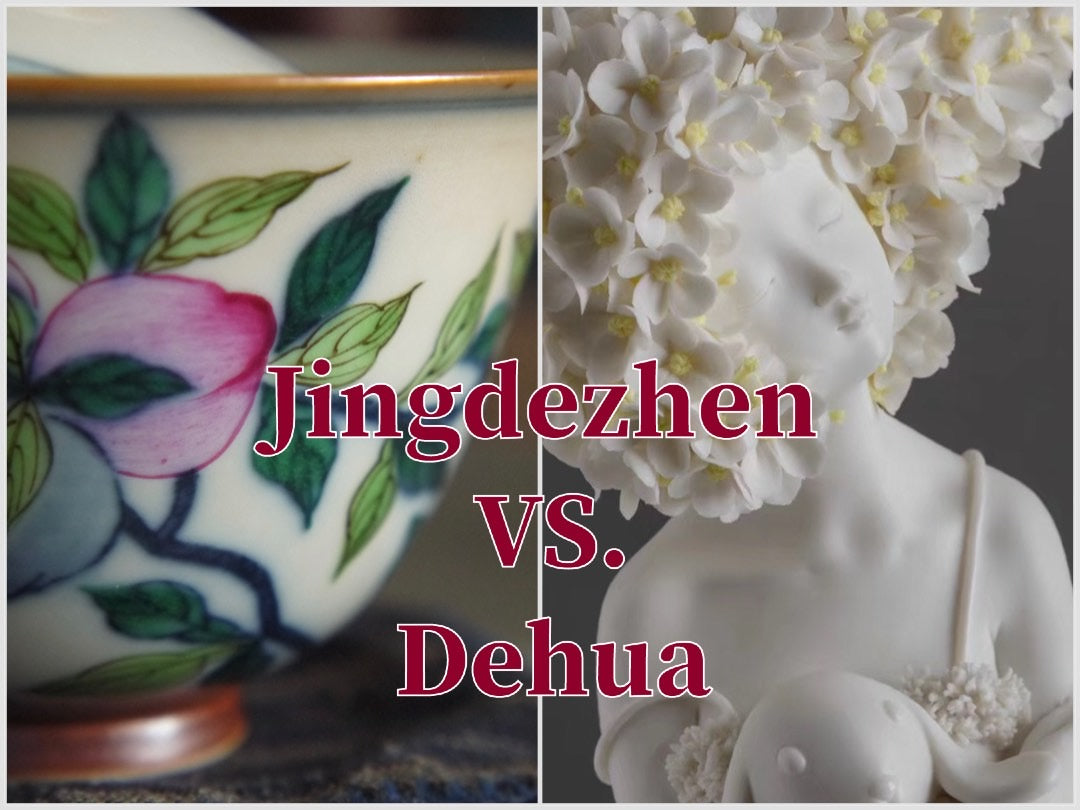
Unveiling the Differences: Dehua and Jingdezhen Porcelain
YuanKevinShare
Dehua and Jingdezhen are two of the most renowned porcelain-producing regions in China, each with unique characteristics that set them apart. These differences can be broadly categorized into three main areas: clay, techniques, and craftsmen.
- Clay
Dehua Porcelain
Dehua is famous for its high-quality kaolin clay, which is exceptionally pure and white. This clay contains very low levels of iron oxide, giving Dehua porcelain its distinctive bright white appearance, often referred to as "Blanc de Chine." The purity of Dehua's clay allows for a smooth, fine texture that is ideal for detailed sculpting and delicate forms.
Jingdezhen Porcelain
Jingdezhen's clay also primarily consists of kaolin, but it has different properties compared to Dehua's clay. Jingdezhen clay includes higher levels of aluminum oxide, which contributes to the porcelain's strength and durability. This type of clay supports the production of a wide range of porcelain types, including the famous blue and white porcelain. Over time, Jingdezhen has had to source kaolin from other regions due to the depletion of local resources.
- Techniques
Dehua Porcelain
Dehua porcelain production involves high firing temperatures similar to those used in Jingdezhen, typically around 1280-1300°C for white porcelain. This high-temperature firing contributes to the porcelain's exceptional quality and durability. Dehua is renowned for its detailed and intricate sculpting of figurines and other artistic forms. Unlike the earlier misconception, Dehua porcelain is not typically bisque fired at lower temperatures; rather, it achieves its fine details and smooth surfaces through skilled craftsmanship and high-temperature firing techniques. This method is particularly suited for creating lifelike religious figures and other sculptures, renowned for their elegance and precision
Jingdezhen Porcelain
Jingdezhen is known for its complex and high-temperature firing processes. A single piece of Jingdezhen porcelain can go through multiple firings, including the initial bisque firing, glazing, and final high-temperature firing at around 1300°C. This results in extremely durable and finely crafted pieces. Jingdezhen is particularly famous for its blue and white porcelain, where cobalt oxide is used to paint intricate designs before glazing and firing. Other notable techniques include famille rose and celadon glazing.
- Craftsmen
Dehua Craftsmen
The craftsmen in Dehua are renowned for their skill in sculpting and carving, producing detailed and expressive works, especially in the form of religious figures. The tradition in Dehua has a strong focus on individual craftsmanship and artistic expression. Each piece often reflects the unique style and skill of the artisan who created it. This approach has been passed down through generations, maintaining a strong link to traditional methods while also integrating contemporary influences.
Jingdezhen Craftsmen
Jingdezhen craftsmen have historically worked within a highly organized system that emphasizes specialization and division of labor. This means that different artisans may focus on specific aspects of production, such as wheel-throwing, glazing, or painting. This division allows for a high level of expertise in each stage of the porcelain-making process. Jingdezhen's reputation for producing imperial porcelain has attracted the best craftsmen over centuries, fostering an environment of innovation and excellence.
- Conclusion
In summary, while both Dehua and Jingdezhen produce high-quality porcelain, their differences lie in the composition of their clay, their production techniques, and the focus of their craftsmen. Dehua excels in creating smooth, white porcelain with detailed sculpting, whereas Jingdezhen is renowned for its high-fired, intricately painted pieces. Understanding these distinctions helps appreciate the unique contributions each region has made to the world of porcelain.




















